APPLICATIONS

The RxClass Browser is a web application for exploring and navigating through the class hierarchies to find the RxNorm drug members associated with each class.
The RxClass API is available for users to include RxClass data in their applications.
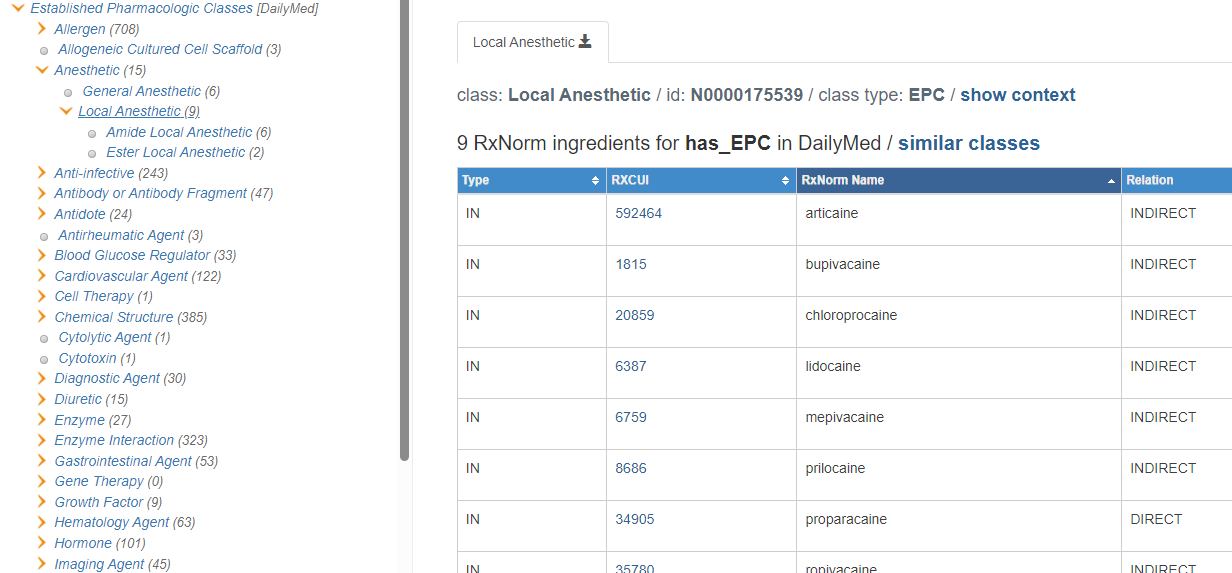
RxClass links drug classes with several drug sources to their RxNorm drug members (usually ingredients, precise ingredients and multiple ingredients).
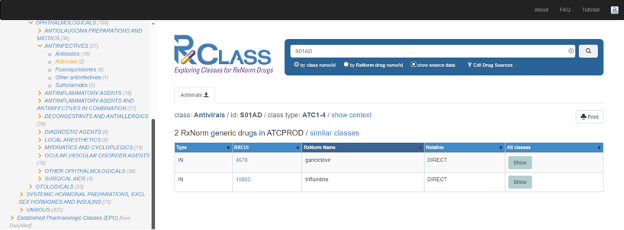
RxClass allows users to search by class name or identifier to find the RxNorm drug members or, conversely, search by RxNorm drug name or identifier to find the classes that the RxNorm drug is a member of.
The RxClass search bar is shown below.
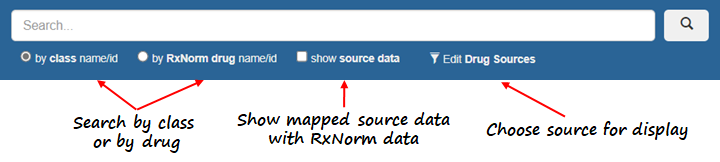
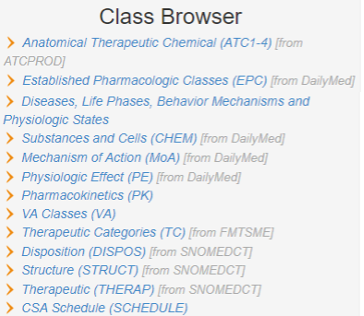
The search by class can be done either by navigating the class tree in the left side of the RxClass window, or by typing in a name in the search box. When typing in a class name, RxClass will give suggestions of class names containing the string. For example, when the term “coxib” is entered in the search box, the following class suggestions are provided:
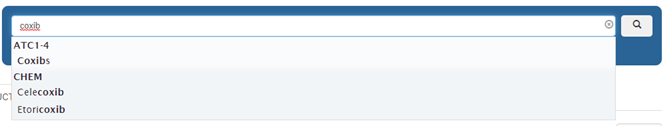
A search by drug name or RxCUI will bring up a pop-up menu containing all the classes the drug is a member of. The example below shows the window when the name “fomivirsen” is entered as a drug name:
While most sources of drug/class relationships relate ingredients to classes, some sources relate products to classes. To facilitate comparison of classes from distinct sources, RxClass ordinarily displays a normalized view of class members as ingredients, transparently translating products to their ingredients. Alternatively, you can view class members as provided by the source, including any ID or name in the mapped vocabulary, by selecting the Show Source Data checkbox.
When the show source data box is checked, additional columns will be displayed in the drug table showing the source data that is mapped into RxNorm. The following images show the tables without and with the source data.
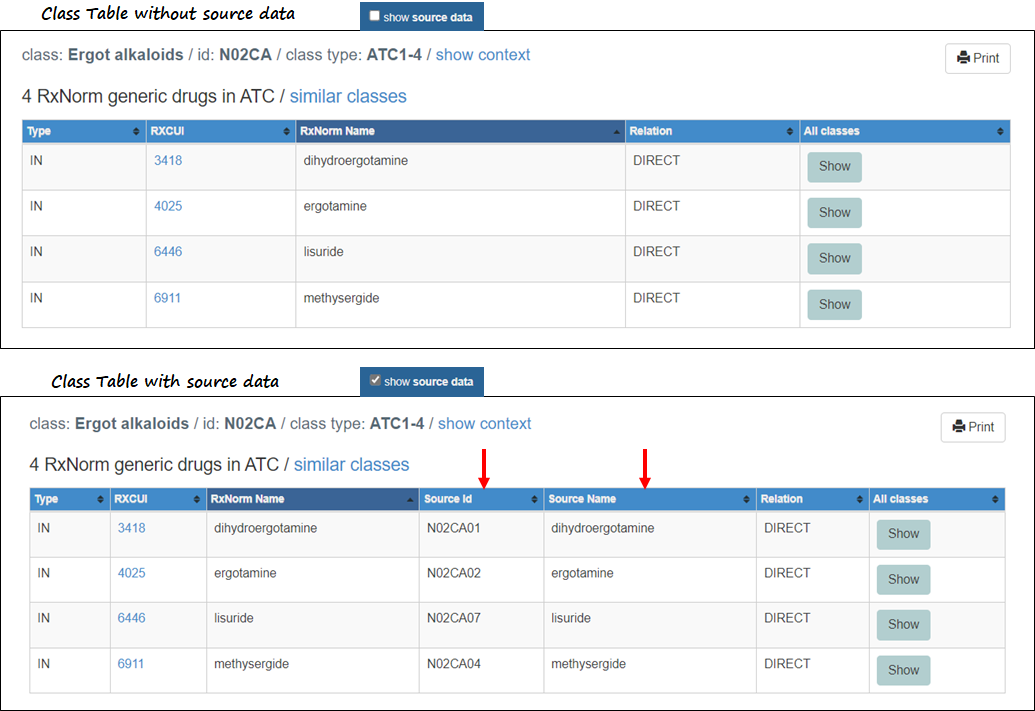
By default, RxClass does not show source data and the drug table(s) are displayed as ingredients. While most drug to class mappings occur at the ingredient level, CSA Schedule, VA and ATC Product map drug products to these classes. When the source data box is checked, for those classes the drug products are shown in the table. For example:
Additionally, once a class is selected, RxClass offers similar classes in drug membership.
| Note: In June 2018, NDF-RT was replaced by MED-RT as a source of drug class relations. Additionally, the VA drug-class relations contained in NDF-RT were replaced by VANDF data. |
SNOMED CT® Usage Conditions RxClass includes SNOMED Clinical Terms® (SNOMED CT®) which is used by permission of the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation (IHTSDO). All rights reserved. SNOMED CT® was originally created by the College of American Pathologists. “SNOMED”, “SNOMED CT” and “SNOMED Clinical Terms” are registered trademarks of the IHTSDO. Use of SNOMED CT in RxClass is subject to the SNOMED CT Affiliate license provisions (incorporated in the License Agreement for Use of the UMLS Metathesaurus as Appendix 2) issued by the National Library of Medicine on behalf of SNOMED International. |
The following table lists the class-member sources available in RxClass for each type of class.
Multiple sources map drugs to some class types. RxClass presents them as alternatives. For example, RxClass shows Chem class members from DailyMed by default, but you may select FDASPL or MEDRT instead, by choosing Edit Drug Sources.
The table below marks with “X” the sources of drug/class mappings, and marks with “X**” the source shown in RxClass by default.
| Class Type | Drug Source | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC | ATCPROD | CDC | DailyMed | FDASPL | FMTSME | MEDRT | RXNORM | SNOMEDCT | VA | |
| ATC1-4 | X | X** | ||||||||
| Chem | X** | X | X | |||||||
| CVX | X** | |||||||||
| Disease | X | |||||||||
| DISPOS | X | |||||||||
| EPC | X** | X | ||||||||
| MoA | X** | X | X | |||||||
| PE | X** | X | X | |||||||
| PK | X | |||||||||
| Schedule | X | |||||||||
| STRUCT | X | |||||||||
| TC | X | |||||||||
| VA | X | |||||||||
| Drug Source | Class Type | Relation | Member Types | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC | ATC1-4 | IN MIN PIN | Drug (ingredient-level) ATC class membership curated by the World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Drug Statistics Methodology | |
| ATCPROD | ATC1-4 | BPCK GPCK SBD SCD | Drug (product-level) ATC class membership curated by the National Library of Medicine | |
| CDC | CVX | isa_CVX | IN, PIN, MIN, SCD, SBD | Drugs in CDC's CVX vaccine groupings |
| DailyMed | EPC | has_EPC | IN MIN PIN | Drug members of a FDA Established Pharmacologic Class |
| DailyMed | Chem | has_Chemical_Structure | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a chemical structure |
| DailyMed | MoA | has_MoA | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Mechanism of Action |
| DailyMed | PE | has_PE | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Physiologic Effect |
| FDASPL | EPC | has_EPC | IN MIN PIN | Drug members of a FDA Established Pharmacologic Class |
| FDASPL | Chem | has_Chemical_Structure | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a chemical structure |
| FDASPL | MoA | has_MoA | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Mechanism of Action |
| FDASPL | PE | has_PE | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Physiologic Effect |
| FMTSME | TC | has_TC | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have Therapeutic Categories |
| MEDRT | Chem | CI_ChemClass | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are contraindicated with a chemical class |
| MEDRT | Chem | has_ingredient | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are members of a chemical class |
| MEDRT | Chem | has_active_metabolites | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have active metabolites in a chemical class |
| MEDRT | Disease | CI_with | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are contraindicated with a disease |
| MEDRT | Disease | induces | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that induce a disease |
| MEDRT | Disease | may_diagnose | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that may diagnose a disease |
| MEDRT | Disease | may_prevent | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that may prevent a disease |
| MEDRT | Disease | may_treat | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that may treat a disease |
| MEDRT | MoA | CI_MoA | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are contraindicated with a Mechanism of Action |
| MEDRT | MoA | has_MoA | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Mechanism of Action |
| MEDRT | PE | CI_PE | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are contraindicated with a Physologic Effect |
| MEDRT | PE | has_PE | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a Physiologic Effect |
| MEDRT | PK | has_PK | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that are members of a Pharmacokinetics Class |
| MEDRT | PK | site_of_metabolism | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a site of metabolism in a Pharmacokinetics Class |
| RXNORM | Schedule | has_schedule | primarily BPCK GPCK SBD SCD; few IN PIN | Drugs that are considered controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) |
| SNOMEDCT | DISPOS | isa_disposition | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a "disposition" (e.g., mechanism of action) |
| SNOMEDCT | STRUCT | isa_structure | IN MIN PIN | Drugs that have a chemical structure |
| VA | VA | has_VAClass | primarily BPCK GPCK SBD SCD SCDF SCDG; few IN MIN PIN | Clinical drugs that are members of a VA Class |
| VA | VA | has_VAClass_extended | GPCK SBD SCD | Related clinical and branded drugs that are derived members of a VA Class. For example, branded drugs related to clinical drugs that are mapped to a VA class, or clinical drugs that have a different dosages from ones that are mapped to a VA class. |