De-Identification of PHI
I. Protected Health Information (PHI)
The Privacy Rule protects all "individually identifiable health information" held or transmitted by a covered entity or its business associate, in any form or media, whether electronic, paper, or oral. The Privacy Rule calls this information "protected health information (PHI)." PHI that is linked based on the following list of 18 identifiers must be treated with special care according to
US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Names
- All geographical subdivisions smaller than a State, including street address, city, county, precinct, zip code, and their equivalent geo codes, except for the initial three digits of a zip code, if according to the current publicly available data from the Bureau of the Census: (1) The geographic unit formed by combining all zip codes with the same three initial digits contains more than 20,000 people; and (2) The initial three digits of a zip code for all such geographic units containing 20,000 or fewer people is changed to 000
- Dates (other than year) for dates directly related to an individual, including birth date, admission date, discharge date, date of death; and all ages over 89 and all elements of dates (including year) indicative of such age, except that such ages and elements may be aggregated into a single category of age 90 or older
- Phone numbers
- Fax numbers
- Electronic mail addresses
- Social Security numbers
- Medical record numbers
- Health plan beneficiary numbers
- Account numbers
- Certificate/license numbers
- Vehicle identifiers and serial numbers, including license plate numbers;
- Device identifiers and serial numbers;
- Web Universal Resource Locators (URLs)
- Internet Protocol (IP) address numbers
- Biometric identifiers, including finger, retinal and voice prints
- Full face photographic images and any comparable images
- Any other unique identifying number, characteristic, or code (note this does not mean the unique code assigned by the investigator to code the data)
II. De-Identification of PHI
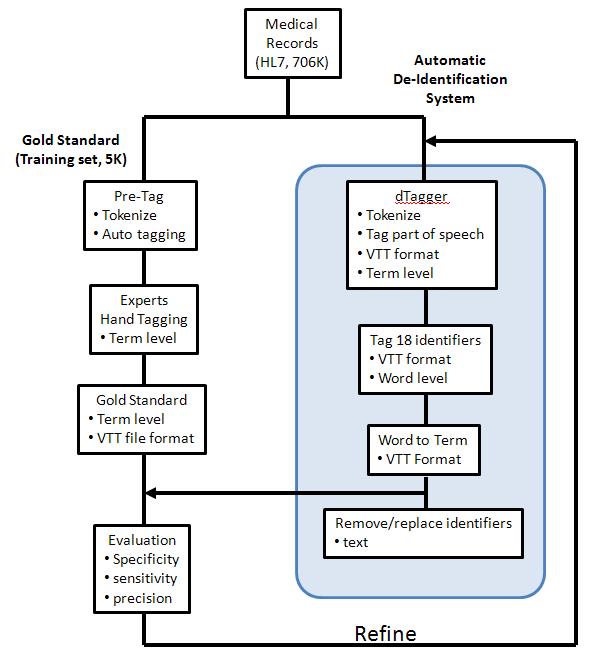
Clinic records are commonly used for Medical research. These data need to be de-Identified before they are used according to the Privacy Rule. To develop a system to remove all above 18 elements of identifiers automatically for PHI is imperative for medical research. The general approach on de-Identification is:
- Define tags for all (18) identifiers
- Tokenize records and tag identifier
- Remove/Replace term with identifiers' tag
In order to evaluate the de-Identification system, a gold standard corpus is needed. The gold standard corpus involves experts hand tag the medical records. The following indexes are used for the evaluation:
- Positive (Identifier); negative (non-identifier)
| Test | Positive | TP | FP (Type I Error) | Positive Predictive value (Precision) = TP / (TP + FP)
|
| Negative | FN (Type II Error) | TN | Negative Predictive value = TN / (FN + TN)
|
| | | Sensitivity (recall) = TP / (TP + FN) | Specificity = TN / (TN + FP) |
|
- Specificity
measures the proportion of negatives which are correctly identified (e.g. the percentage of non-identifier terms that are tagged as non-identifiers).
specificity = (number of True Negatives) / (number of True Negatives + number of False Positives)
- Sensitivity (recall rate)
measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such (e.g. the percentage of identifier terms that are tagged as identifier)
sensitivity = (number of True Positives) / (number of True Positives + number of False Negatives)
- Precision (Positive predictive value)
a measure of exactness or fidelity
precision = (number of relevant documents retrieved) / (total number of documents retrieved)
precision = (number of True Positives) / (number of True Positives + number of false Positives)
- Recall
a measure of completeness
recall = (number of relevant documents retrieved) / (total number of existing relevant documents, which should have been retrieved )
recall = (number of True Positives) / (number of True Positives + number of False Negatives)
III. How VTT is used?
First, VTT is used as a tool for hand tagging medical records for the gold standard data set. VTT provides GUI to ease the human tagging process by showing tagged text in different visual styles (colors, fonts, sizes, etc..)
Second, VTT read and write tags, markups for a specified text from and to a file in VTT file format. This VTT file format is also used in developing auto de-Identification programs.
A schematic diagram bellow shows a typical de-Identification developing project using VTT.